Gastroscopy
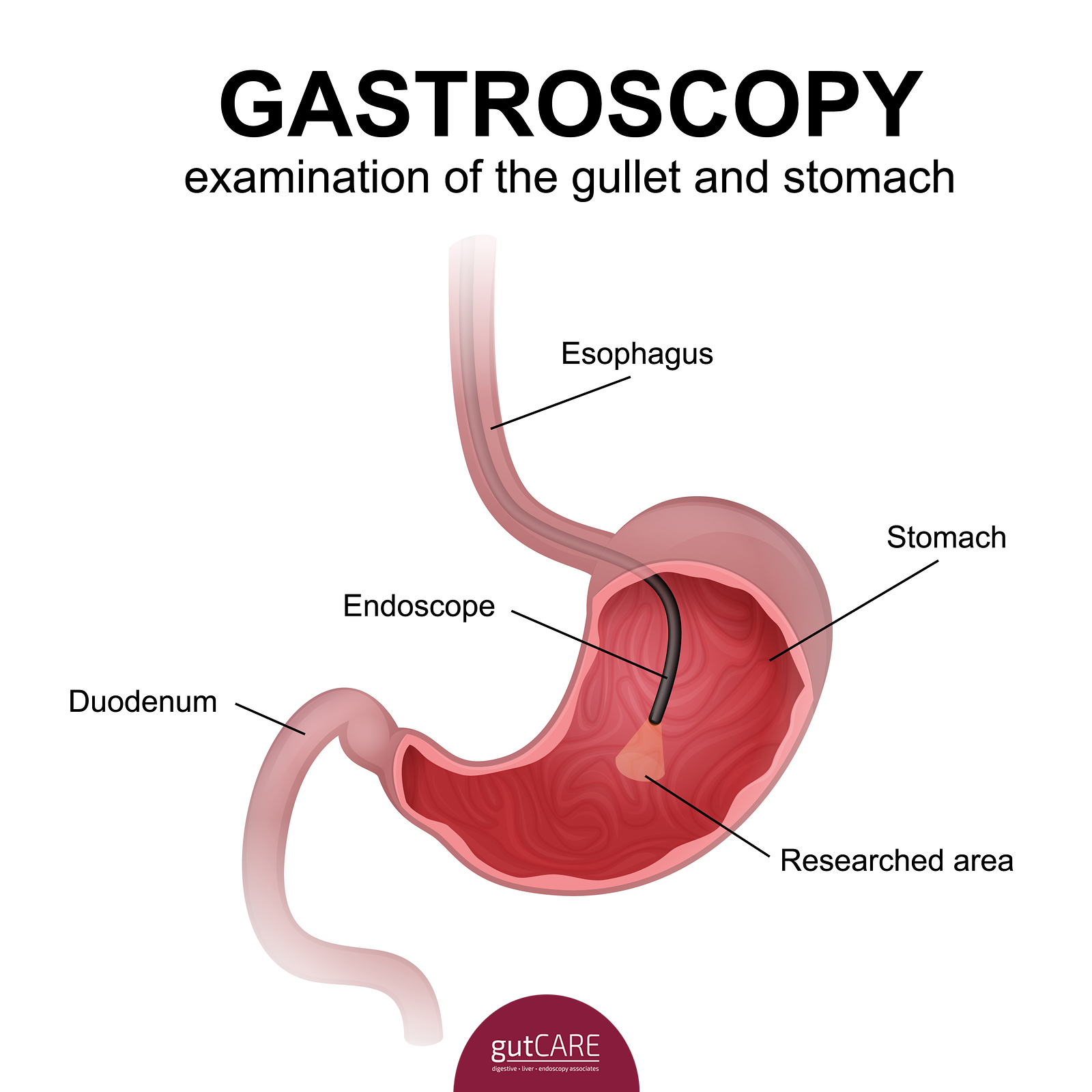
What is a Gastroscopy?
A colonoscopy is a test that allows your doctor to examine the lining of your colon for any abnormalities. The colonoscope, which is a thin,flexible, fiber optic instrument, is passed from your rectum to your cecum.
Colonoscopy is considered the “gold standard” to evaluate intestinal inflammation, ulceration, bleeding, diverticulosis and tumors. It is possible to remove most colon polyps during a colonoscopy, there is no pain or any sensation as the polyp is removed.
What is a Gastrostomy?
The food we eat reaches the stomach, which is in the upper part of the abdomen. In your case, your doctor has recommended a direct access for feeding into the stomach. This means a tube will be placed surgically, so that one end remains inside the stomach. The other come out of the abdominal wall. It is meant to provide a route to introduce liquid food directly into your stomach.
What care should I take of the tube?
After surgery, you may not need to care for the tube, as the doctor may see the dressing daily for a week. By about a week, he will need to loosen the retention plate a little, so there will be some “play” between the inner Retention Plate & the outer Fixation Plate. The appliance is easier to dress after that.
You can safely take a head bath as early as about 4 days after surgery. While bathing, you can wash the area around the tube with soap and water, and dry it with your towel, the skin close to the tube may be cleaned with surgical spirit; this is so as spirit will evaporate quickly. No ointments should be applied on or near the parts of the tube – they may damage the material durability.
Every 2 to 3 days the Fixation Plate should be loosened, the tube should be pushed into the stomach for 3-4 cm, the tube rotated slightly & fixed again with very little tension on a thin dressing. Once you get the confidence by seeing your doctor doing this, you could take over and keep doing it yourself!
After putting in feeds, it tubes up to 2-3 hours for the feed to empty completely from the stomach. So, after taking feeds, make sure the stoppers at the feeding end are well closed to prevent a leak onto your clothes. You may then keep the outer end of the tube facing in any position, it does not matter; just take care there is no tension on it at any time. You may even sleep on your stomach, when the tube is in.
What are the parts of the tube?
We can start describing the tube from the part inside the stomach till the outer Feeding End.The part of the tube inside the stomach has a Silicone Retention Plate. This will not allow the tube to accidentally come out.On the skin where it comes out, the tube is held by a silicone (white, triangular) External Fixation Plate.A Tube Clamp may be used to block it when not in use.At the Feeding End of the tube, you can attach 2 types of adapters to help make feeding easy.
[a] Universal feeding adapter [violet or blue color] – that can accept a syringe or a feeding funnel. The Adapter screws onto the Luer lock connector ; the Connector is fixed onto the tube with a fixing screw.
[b] Funnel connector [violet color] – that accepts a funnel for feeding. It has its own fixing screw for the tube.
How should feeding be done?
You should be able to give yourself all the feeds independently! Get used to handling large volume syringes (like ones with a 50 ml capacity). You could use the syringe as the nurses do – draw the feed into the syringe by pulling back the plunger; or; you could remove the plunger from the barrel of the syringe, and pour the feed directly into it, like as if it is a funnel. Be careful to see that the syringe is at least 4-5 inches above the level of the stomach; so the feed flows by gravity.
Always wash your hands carefully before starting to feed as well as after feeding. Always take tube feeds in sitting or semi reclining position (never lying down). Before starting feeding confirm that the tube is patent (the passage is open) by gently pushing 20 ml drinking water gently through it. You should also flush the tube after feeding, and confirm there are no particles seen in it, as well as the flow in unobstructed. Remember to wash all re-usable appliances; you could get a diarrhea in case germs get in with the next feed. In case the plunger of the syringe fits tight on re introducing, you could lubricate it with vegetable oil.
To facilitate feeding there are appliances for attachment to the tube. Deciding an appliance will need you can classify all your liquid meals henceforth into two types-
- Watery thin liquids may be directly poured into the barrel of the syringe, so the barrel of the syringe acts as a funnel and the liquid drains in by gravity.
Thick fluids may need to be aspirated (pulled) into the syringe and then pushed gently after fixing the syringe onto the Universal Feeding Adapter.
How should choose what to use as a feed?
It is always better to follow the advice of a dietitian to decide what, and how much, should be used as a feed. They, in consultation with your doctors, are the best to decide what will be digested best at which time of the day: as well as what is best avoided at certain times (like what may cause “acidity” at night).
When we are forced to choose foods in liquid form, we may tend to choose more of easily available liquids like milk and fruit juices. Some persons get loose motions if give beyond a tolerable amount of such liquids at a time or in the day.
Feeds too rich in sugar may cause a sense of drowsiness, and very thick feed s may “sit like a rock” for a long time. If the feed prescribed dose not flow easily, ask your dietitian for help. Diluting the feed on your own may make it less nutritious. Some persons may have a restriction on the amount of water they can take per day. Never keep a feed prepared for use beyond 4-6 hours, it may get contaminated and give you a diarrhea.
Does the feeding tube have a chance of getting blocked?
Does the feeding tube have a chance of getting blocked?
Different food ingredients as well as medicines are chemicals: some may suddenly clot to form a thick paste when they meet (Coagulate). So it is better to flush the tube between every two types of feeds and not allow them to mix in the tube.
Fruit juices (contain citric acid) & tea (containing tannic acid) are common examples of what can start problems . Milk ,buttermilk and milk shakes should be strained of the cream before feeding. Antacid medications should never mixed with food. When the doctor writes you a prescription anytime, always remember to remind him to offer a syrup or a liquid suspension of a medicines than a tablet, if it is available. Your doctor will take a call on what to do if a medicine is available only as a capsule. Some medicines like cough syrups contain alcohol: be sure to flush the tube to protect it.
ljbwekhbvksbigviwegiewgiwgeUt elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
