Anal Canal
What is a Anal Canal?
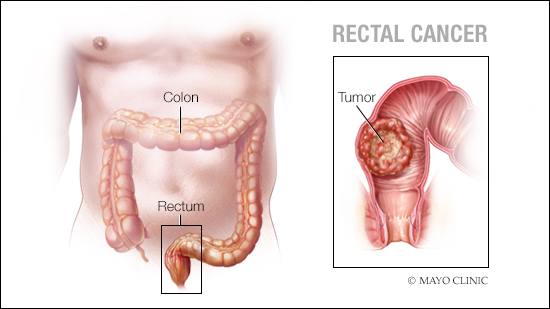
Anal cancer is an uncommon type of cancer that occurs in the anal canal. The anal canal is a short tube at the end of your rectum through which stool leaves your body.
Anal cancer can cause signs and symptoms such as rectal bleeding and anal pain.
Most people with anal cancer are treated with a combination of chemotherapy and radiation. Though combining anal cancer treatments increases the chance of a cure, the combined treatments also increase the risk of side effects.
Symptoms
Anal cancer signs and symptoms include:
- Bleeding from the anus or rectum
- Pain in the area of the anus
- A mass or growth in the anal canal
- Anal itching
Causes
Anal cancer forms when a genetic mutation turns normal, healthy cells into abnormal cells. Healthy cells grow and multiply at a set rate, eventually dying at a set time. Abnormal cells grow and multiply out of control, and they don’t die. The accumulating abnormal cells form a mass (tumor). Cancer cells invade nearby tissues and can separate from an initial tumor to spread elsewhere in the body (metastasize).
Anal cancer is closely related to a sexually transmitted infection called human papillomavirus (HPV). Evidence of HPV is detected in the majority of anal cancers. HPV is thought to be the most common cause of anal cancers.
Risk factors
Several factors have been found to increase the risk of anal cancer, including:
- Older age. Most cases of anal cancer occur in people age 50 and older.
- Many sexual partners. People who have many sexual partners over their lifetimes have a greater risk of anal cancer.
- Anal sex. People who engage in receptive anal sex have an increased risk of anal cancer.
- Smoking. Smoking cigarettes may increase your risk of anal cancer.
- History of cancer. Those who have had cervical, vulvar or vaginal cancer have an increased risk of anal cancer.
- Human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV infection increases your risk of several cancers, including anal cancer and cervical cancer. HPV infection is a sexually transmitted infection that can also cause genital warts.
- Drugs or conditions that suppress your immune system. People who take drugs to suppress their immune systems (immunosuppressive drugs), including people who have received organ transplants, may have an increased risk of anal cancer. HIV — the virus that causes AIDS — suppresses the immune system and increases the risk of anal cancer.
Prevention
There is no sure way to prevent anal cancer. To reduce your risk of anal cancer:
- Practice safer sex. Practicing safe sex may help prevent HPV and HIV, two sexually transmitted viruses that may increase your risk of anal cancer. If you choose to have anal sex, use condoms.
- Get vaccinated against HPV. A vaccine to protect against HPV infection is available. It’s recommended for adolescents, including both boys and girls, but may be given to adults, too.
- Stop smoking. Smoking increases your risk of anal cancer. Don’t start smoking. Stop if you currently smoke.
